Table Of Content
- First Engine Started on Massive New Royal Caribbean Cruise Ship
- What Happens to the Heat From a Cruise Ship’s Engine?
- Harvesting Solar Energy Way of the Future
- Cruise Ship Engine Technology
- Diesel-Electric Cruise Ship Engines
- Biggest Ship Propellers in the World
- If Cruise Ships Have Engine Failure: What to Expect

Emissions from cruise ship engines contribute to air pollution and climate change. Key pollutants include sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. COGAS systems are commonly used in larger cruise ships due to their enhanced efficiency and power output capabilities. These systems provide the necessary propulsion and electricity generation, supporting the operation of various onboard facilities and amenities. It's increasingly rare that modern ships, which are built to high standards and specifications and are maintained at high levels, will experience engine failure.
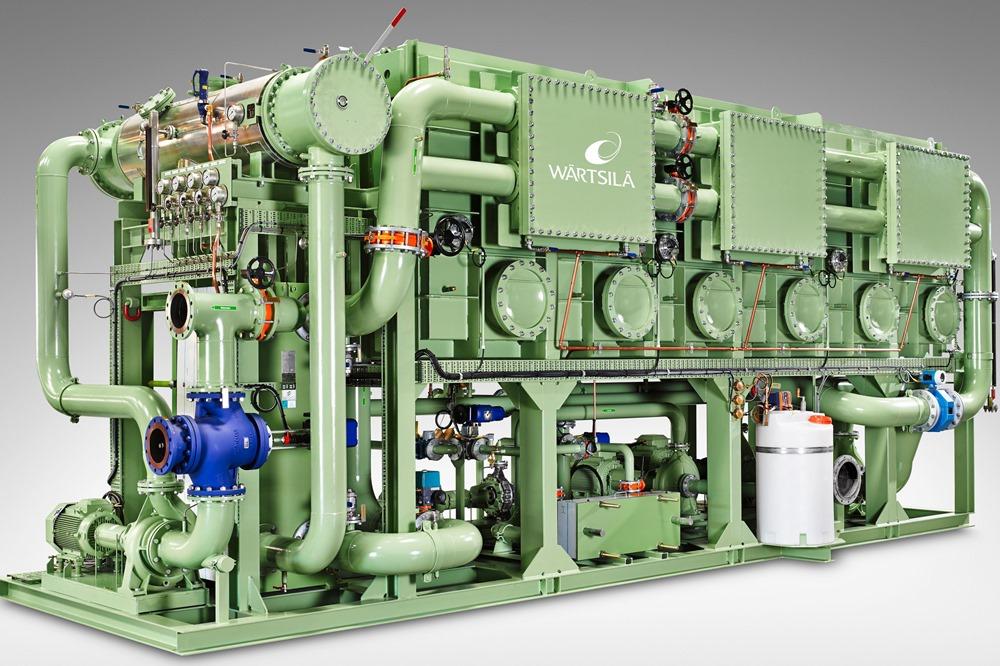
First Engine Started on Massive New Royal Caribbean Cruise Ship
While berthed, the ship was successfully provided with LNG at all the itinerary's ports of call (Hamburg, Rotterdam, Le Havre, Southampton, Zeebrugge). The aptly named Celebrity Cruises treats all passengers like A-listers. And they’ve won numerous awards for not just being LGBTQ-friendly but for being totally inclusive and wholeheartedly embracing and encouraging diversity. A unique, fun and educational option for families with older kids who want to experience nature with a touch of Disney magic, these expedition cruises are the stuff of lifelong memories. Small, purpose-built ships are designed to access the remote landscapes of the Polar Regions and the Galápagos Islands—and to appeal to both kids and adults.
What Happens to the Heat From a Cruise Ship’s Engine?
However, cruise ships use sound-dampening technology and insulation to minimize noise pollution. In the past, cruise ships kept their engines running while docked to generate electricity for shipwide services. Despite their advantages, gas propulsion is not widely used in the cruise industry. Gas-powered ships are faster, but most cruise ships don’t travel faster than knots.
Harvesting Solar Energy Way of the Future
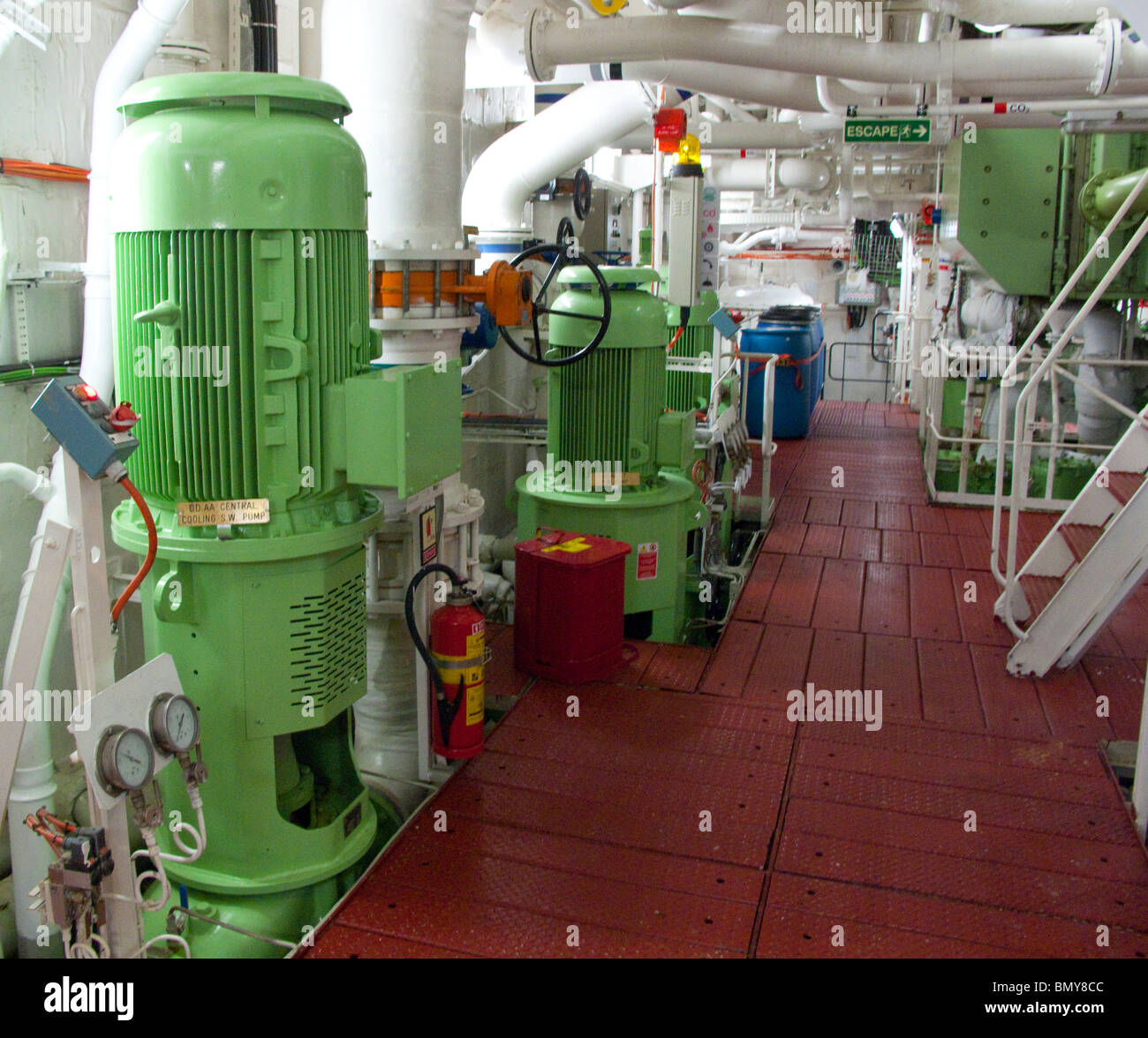
Crew members can monitor the ship’s systems from the engine control room. From the operation control center, crew members monitor the ship’s systems and act as a central area for maintaining the technical equipment on the cruise ship. Cruise ship fuel tanks are also on the lower decks, but they are kept separate from the main engines. The engine rooms on cruise ships are located on the lower decks, between the midship and the aft. The engines aren’t quite at the back of the vessel but closer to midship. Waste heat from the cruise ship’s engines is extracted by a series of heat exchangers located on the exhaust path after the turbochargers en-route to the scrubber.
The generators can operate critical navigation systems, emergency lights, and other vital equipment. We’ll cover some of the most popular technologies used by cruise ships. For example, one person may be responsible for the freshwater generators and water pumps and another for the fuel oil systems. Every piece of equipment can be monitored from the engine control room to ensure the cruise ship runs smoothly. There are several reasons for keeping the cruise ship engine room away from passenger areas.

Whether you are curious about a cruise ship’s engine or simply want to avoid the cabins surrounding this noisy area, an engine room can be an interesting place. Power cables from the HV switchboard connect to the PEM in a conventional DE propulsion system, which converts the electrical power to mechanical power. It then gets transmitted to the propellers with the help of lengthy shaft lines, bearings and thrust blocks. There are around 100 cruise ships that have embraced this technology. These include Royal Caribbean International’s Oasis-class ships Oasis of the Seas, Symphony of the Seas, Harmony of the Seas and Allure of the Seas, to name a few.
Biggest Ship Propellers in the World
The recovered heat is typically used for a number of services, including fuel heating (if using heavy fuel oil) and the desalination of saltwater into freshwater by an evaporator plant. Fresh water is also produced by reverse osmosis to supplement the evaporator. The biggest ships like Royal Caribbean’s Oasis-class ships have six engines and most other cruise ships have four. Most often, especially in newer cruise ships, the engines are located on the lower decks and towards the aft of the ship.
World's largest cruise ship sets sail, bringing concerns about methane emissions - Reuters
World's largest cruise ship sets sail, bringing concerns about methane emissions.
Posted: Sun, 28 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
While it won't be for awhile, we are looking forward to when the fifth Edge Class ship's flex fuel engine is started up for the first time. On March 15, the Meyer Turku shipyard, where Icon of the Seas is being built, confirmed that the first multi-fuel engine was turned on for the first time! This was huge news for Royal Caribbean and Royal Caribbean Group alike. "As we innovate our ship design and offerings, we're also focused on equally evolving the fuel and technology landscape that powers them," said Jason Liberty, president and CEO, Royal Caribbean Group. With the complex technology involved, it’s a huge milestone for the workers at the shipyard. It shows that the installation has succeeded, which is especially important for a new design.
These backup generators are always located higher up and outside the engine room spaces to insulate them from fire or damage to the engine room. Big ships require so much power that they might have two or more emergency generators. Even so, they will not have anywhere near the capacity of the main engines and generators. They don't produce enough electricity to move the ship, and they can't even supply all the limited power needed in port, mostly because of space constraints.
LNG tanks are two (type C / vacuum insulated), each with capacity 200 m3 and weight 140 tons (LNG weight 85 tons per tank). Main engines and generators require electricity and it's needed to keep them going. Pumps that are driven electrically take in cold ocean water to cool the engines and electrical pumps get fuel from fuel tanks and supply it to the engine. Electrical power is vital for many operational functions - without it, ships come to a halt.
Diesel engines are commonly used in cruise ships due to their efficiency and reliability. They provide the necessary power for propulsion and onboard systems while ensuring fuel economy and compliance with environmental regulations. Gas turbine engines offer high power output and quick response, making them suitable for high-speed cruise ships. Combined Gas and Steam Turbine Engines (COGAS) provide efficient power generation and improved fuel economy by utilizing waste heat to produce steam.
When ships come into port, they take the opportunity to fill up the fuel tanks. Fueling barges will come up to the ships and load the fuel onboard. When the passengers return from their excursions, the ship is ready to move on. How much is dependent on the size of the ship, the speed it goes, and the distance it travels. The amount of fuel an average cruise ship goes through in a voyage is generally around 300 tons a day. The electricity generated from the diesel-electric method can also be used onboard.
For example, Queen Mary 2 consumes 237 tons MGO and 261 tons HFO a day when at full speed. After a certain point, the rate of return decreases from adding engines, because if a ship can manage 17 knots by two engines, it doesn't mean that four engines are going to produce 34 knots. MS Viking Grace is also the world's first ship with the energy recycling system "Ocean Marine" (developed by Climeon AB / Stockholm-based company). The system converts the excess heat (generated by engines and exhausts) into clean (emission-free) electricity with an annual capacity of 700,000 kWh. This electricity is primarily used on cabin decks (including for heating, hot water, lighting).
Each of the Star Cruises "Global-Class" vessels have three "Azipod XO" thrusters. All ships have installed ABB's "Intelligent Maneuvering Interface" and the "OCTOPUS" software optimizing fuel consumption and energy management. All these ships were constructed by the German shipbuilder MV Werften. Currently, almost 2/3 of all large-sized cruise vessels, icebreaking ships, and high ice-class cargo ships are with Azipod propulsion. Large equipment (propulsion motor, bow thrusters) requires electricity of high voltage.
Overall, gas turbine engines provide an efficient and powerful option for cruise ships, particularly those focusing on high-speed travel. Their ability to quickly respond to power demands and lower emissions make them a valuable choice for enhancing the overall cruising experience. The latest generation of cruise ships are equipped with diesel electric engines. Instead of the more traditional engine-shaft-propeller arrangement, in this case the engines are connected to generators to create electricity. The generators power electric motors, and the electric motors move the propellers. The main engines and even the generators themselves require electricity to keep going.
No comments:
Post a Comment